
In both cases, the difference was smaller than the rank() function, but the PG15 still showed better results, as seen in the trend line. I also got the results from 500 executions for these last two functions. I did the same exercise for the row_number() and count() functions. We see the PG13 performed the “ worst ,” and even when the PG14 showed a better trend, the PG15 was the best. We can see the timing from the PG15 version is better than the other versions. To verify this is consistent, I got the Total Time for the WindowAgg node from 500 executions and plotted the next graph.
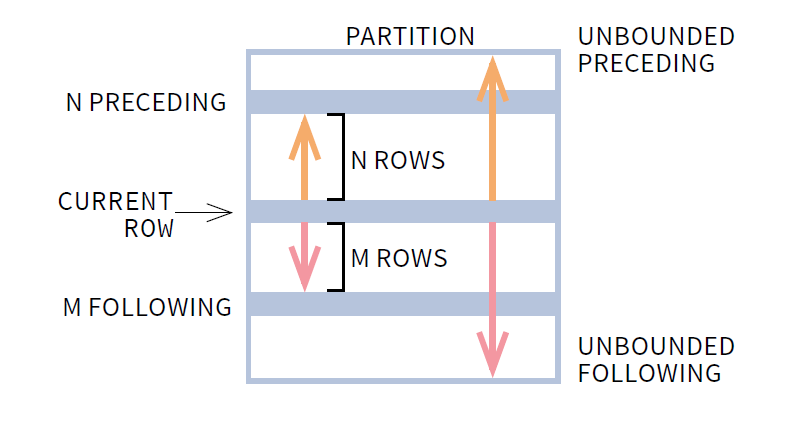
The performance improvement is clear here. We can easily see from the WindowAgg node that the total time was smaller in the PG15 than in the other two. Returns the current row number within its partition, counting from 1. Returns the rank of the current row, with gaps that is, the row_number of the first row in its peer group. As we read in the documentation, the named functions work for: The “set of table rows” is usually identified as a “partition” defined by a column or columns. The window functionsĪs mentioned above, the window functions let us perform some calculations on a set of table rows related to the current one. First, let’s review what these functions can do. In the latest release, PostgreSQL 15, some performance improvements were added for the rank(), row_number(), and count() functions.
Postgresql window functions windows#
There are several built-in windows functions available in PostgreSQL. Usually, these tasks leverage window functions to do calculations “across a set of table rows that are somehow related to the current row,” as is described in the documentation. When working with databases, there are always some projects oriented to performing analytics and reporting tasks over the information stored in the database.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
